Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease and the Gut Gel Method
The intestinal gel method developed for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease could be a hope for patients. This method can help reduce symptoms by allowing drugs to be absorbed into the body more effectively and quickly.

Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease
Associate Professor Dr. Yakup Türkel, a neurology specialist, provided information about an innovative method used in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease called intestinal gel therapy. He mentioned that patients are fitted with a permanent percutaneous endoscopic gastrojejunostomy (PEG-J) system with an intestinal tube attached to the external end of the tube connected to an intestinal gel pump. He emphasized that thanks to this method, patients can lead their daily lives more comfortably and reduce their need for medication.
Patient Story
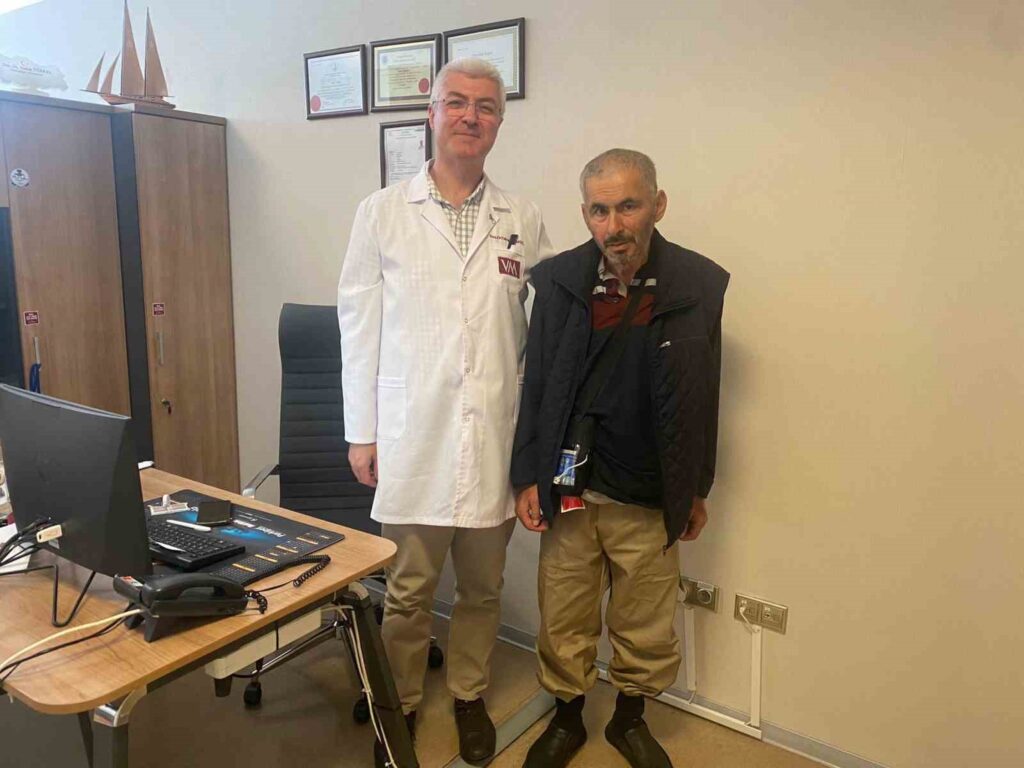
The intestinal gel therapy applied to a 57-year-old patient battling Parkinson’s disease for 5 years at VM Medical Park Samsun Hospital has yielded positive results. The patient initially presented with symptoms of slowing down and tremors, but after the treatment, he became able to meet his own needs. Associate Professor Dr. Yakup Türkel stated that intestinal gel therapy holds an important place among device-assisted treatments applied in advanced stages of the disease.
Continuing his statements by saying, “Advanced-stage Parkinson’s disease is a condition where despite receiving medication in sufficient doses and duration, the effect of the drug is short-lived, periods of wellness and sickness alternate, the quality of good periods is low, and there are involuntary movements,” Associate Professor Dr. Yakup Türkel indicated that different treatment options are evaluated based on the patients’ conditions and that intestinal gel therapy has been applied as an effective method in recent years.
- Intestinal gel therapy can be preferred when the effect of the medication diminishes.
- Intestinal gel therapy provides convenience in the daily lives of patients.
- Patient stories highlight the success of intestinal gel therapy.